The Sherman Homeowner's Guide to Garage Door Health
Published: Feb 17, 2026
That sudden screech, the shuddering halt, the groan that echoes through the house—your garage door has a language all its own. For most Sherman homeowners, it’s a language of inconvenience and mystery. You know something’s wrong, but what is it trying to tell you? Is it a simple fix or a sign of something more serious?
You’re not alone in asking these questions. Your garage door is the largest moving part of your home, a complex system of springs, cables, and electronics working in harmony. When that harmony is disrupted, it can feel overwhelming.
This guide is your translator. We’ll demystify the noises, explain the core components, and give you the knowledge to make confident decisions. Consider this your first step from being a confused browser to an empowered homeowner.
Foundation: Core Concepts Simply Explained
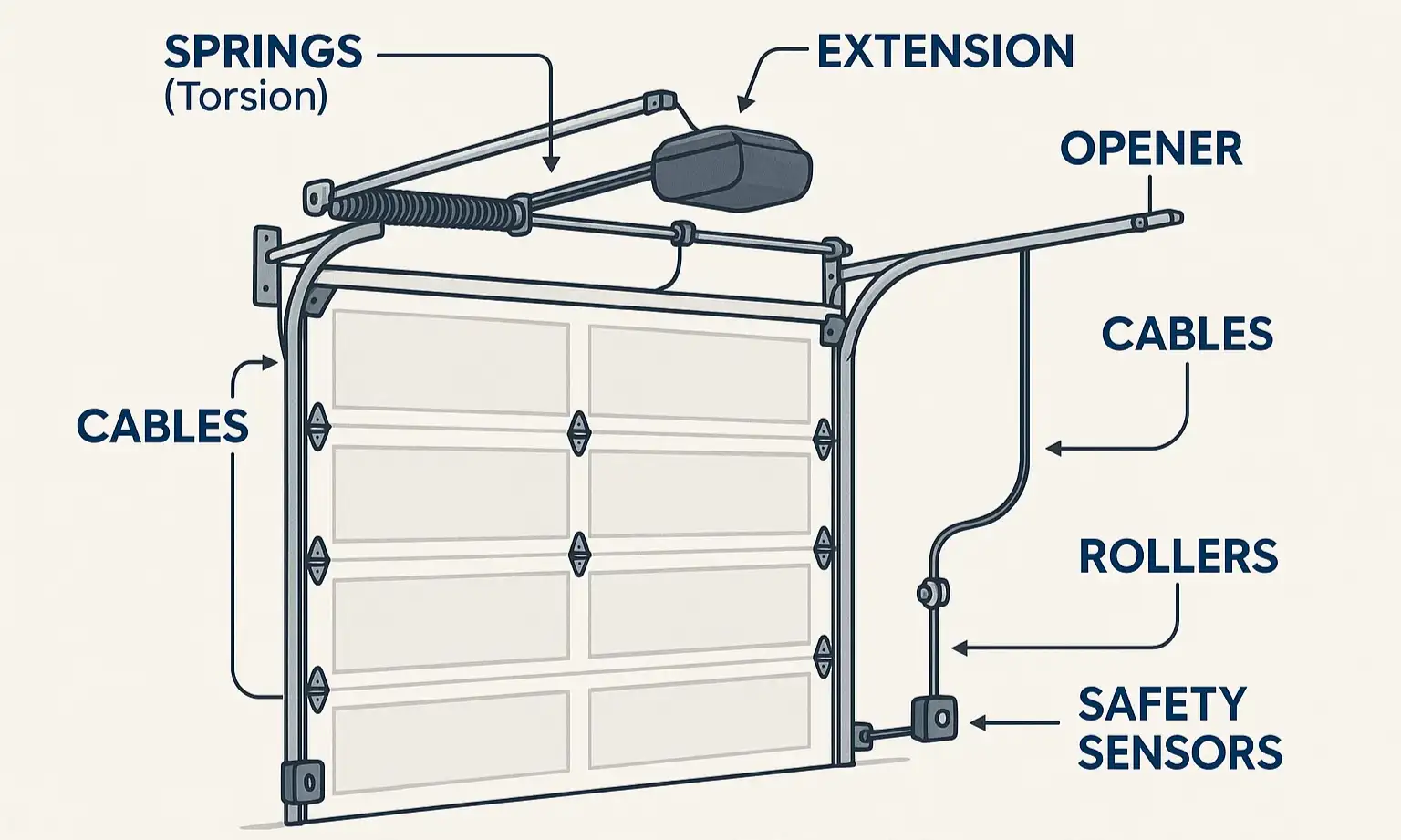
The Anatomy of Your Garage Door
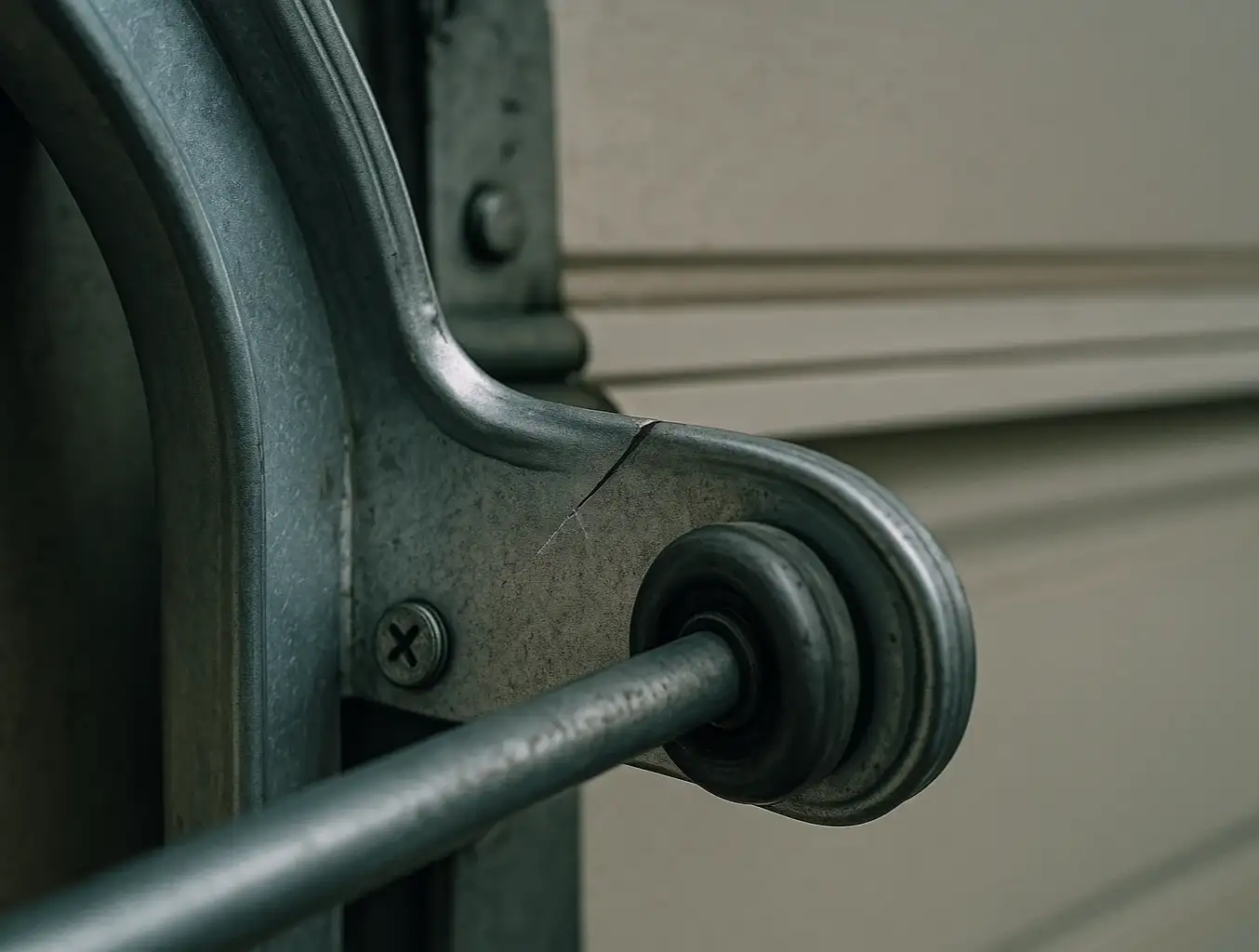
- The Springs (The Muscle): This is the most important—and dangerous—part of the system. Whether you have large torsion springs on a bar above the door or long extension springs along the sides, their job is to do the heavy lifting. The springs, not the opener, are what make your 200-500 pound door feel light enough to lift.
- The Opener (The Brain): This is the motorized unit that controls the door's movement. It receives the signal from your remote or keypad and initiates the open/close cycle, working with the springs to guide the door along the tracks.
- The Cables (The Ligaments): These high-tension steel cables connect the springs to the bottom of the door. They transfer the immense energy from the springs to lift the door evenly and safely. If one snaps, the door can become crooked and dangerously unstable.
- The Rollers & Tracks (The Skeleton): The rollers are the wheels that sit in the metal tracks on each side of your door, guiding it up and down. Worn-out or broken rollers are often the source of those loud, grinding noises.
- The Safety Sensors (The Eyes): Located near the bottom of the track, these two small sensors shoot an invisible beam of light across the opening. If anything breaks that beam while the door is closing, the opener will automatically reverse, preventing accidents.

Building: Diagnosis & Decision-Making

Common Garage Door Problems and What They Mean
The DIY Danger Zone: Repairs You Should Never Attempt

Need more information?
Get a free quote
Mastery: Prevention & Upgrades
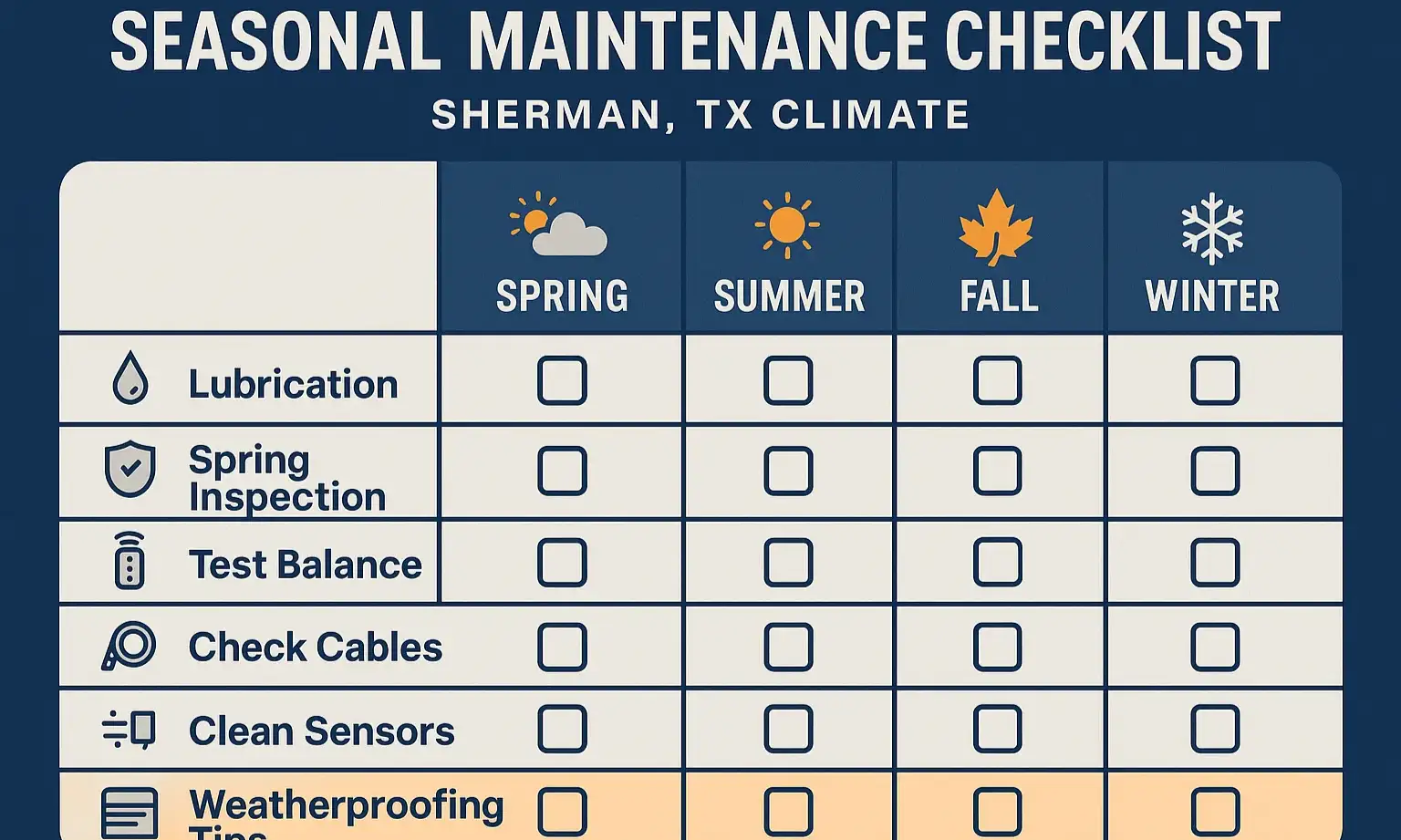
The Ultimate Maintenance Checklist for North Texas Weather
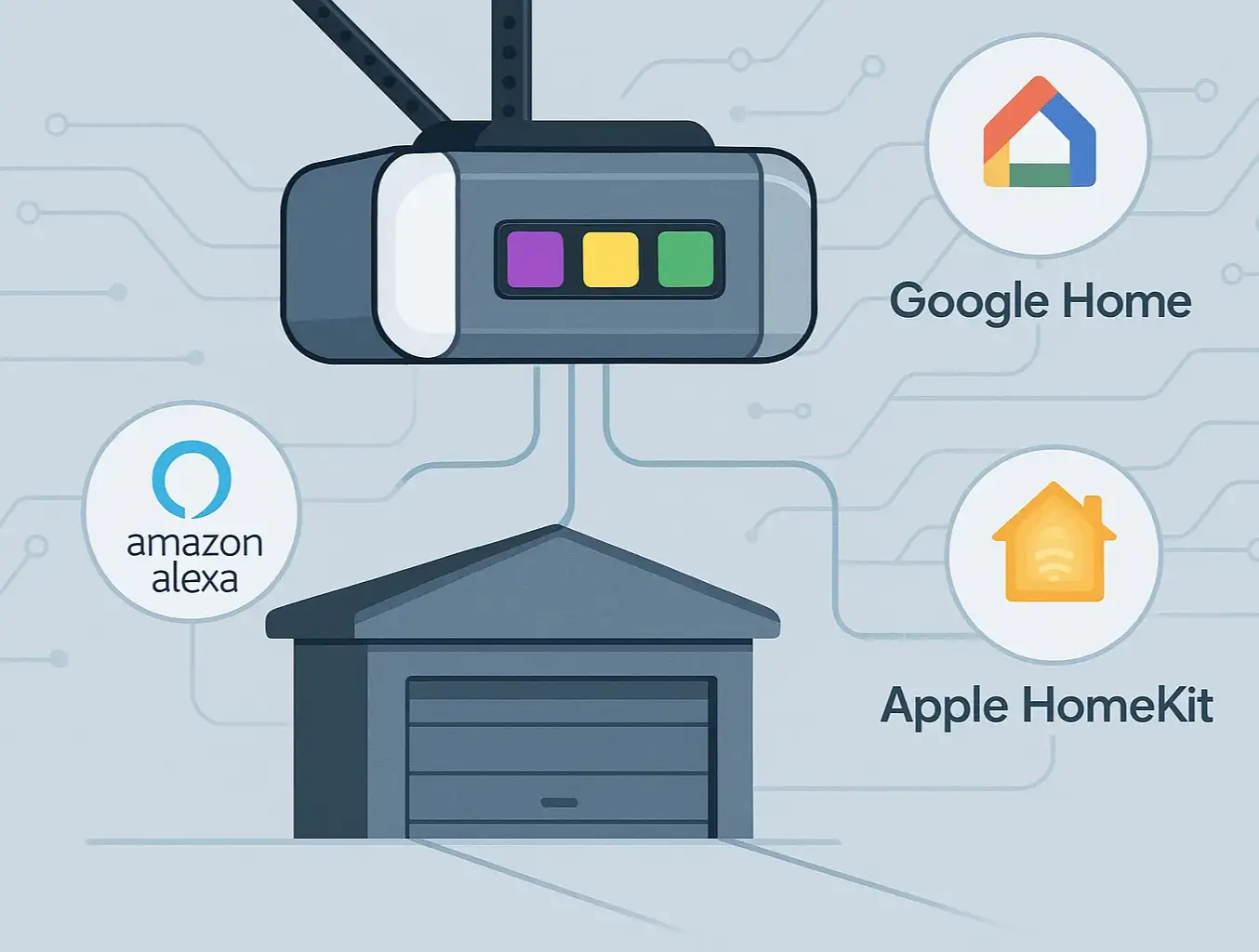
Is a Smart Opener Right for You?
- Smartphone Control: Open, close, and check the status of your door from anywhere.
- Delivery Access: Grant temporary or secure in-garage delivery access for packages.
- Activity Alerts: Get notifications on your phone whenever the door is used.
- Voice Commands: Integrate with systems like Alexa or Google Assistant.

Frequently Asked Questions
What is the most common problem with garage doors?
Can I manually lift my garage door if the spring is broken?
Do you need a license to repair garage doors in Texas?
Your Next Step
You may also like